Let’s research!【No.2】Student Conference on Global Innovation and Partnershipでの研究発表
王ゼミでは、金融教育と英語教育を融合する教育を実践しています。毎年、複数の英語プロジェクトに参加し、外国・他大学の学生と切磋琢磨することがその重要な一環です。
2015年1月に、ゼミ生25名がStudent Conference on Global Innovation and Partnership(→こちら)に参加し、金融関連のテーマについて、英語でポスタープレゼンテーションを行いました。
皆さんにとっての人生初の英語プレゼンでしたが、全員の発表はとても堂々としていました。I’m so proud of you, boys and girls!
ここでは、発表内容(一部)を紹介します。
発表タイトル一覧:
1. What is a portfolio?
2. What is the stock market?
3. What is financial investment?
4. How customers choose banks?
5. Foreign Direct Investment
6. Future Possibilities of Venture Companies
7. Factors Affecting Economic Growth
8. What are the economic benefits of intangible assets?
2015年1月に、ゼミ生25名がStudent Conference on Global Innovation and Partnership(→こちら)に参加し、金融関連のテーマについて、英語でポスタープレゼンテーションを行いました。
皆さんにとっての人生初の英語プレゼンでしたが、全員の発表はとても堂々としていました。I’m so proud of you, boys and girls!
ここでは、発表内容(一部)を紹介します。
発表タイトル一覧:
1. What is a portfolio?
2. What is the stock market?
3. What is financial investment?
4. How customers choose banks?
5. Foreign Direct Investment
6. Future Possibilities of Venture Companies
7. Factors Affecting Economic Growth
8. What are the economic benefits of intangible assets?
Future Possibilities of Venture Companies (Juniors: Hiroaki Fujisawa, Oyonna and Itsuki Hamaguchi)
The subject of our presentation is future possibilities of venture companies. Venture companies are companies which are trying to make innovations. But there is no clear definition actually. If a large company created an innovation, people don’t call the company a venture company. The point is how small and how young the company is. If a small and young company is innovative in business, uses its originality to produce original products, and develops new technology, then this company can be regarded as a venture company. There are many venture companies in Japan. For example, Cyber Agent, GREE are good examples. Many Japanese venture companies are related to the internet.
Developing new technology and making new products are important and necessary for venture companies. If their businesses are becoming successful, the venture companies also want to go IPO. IPO means Initial Public Offering. By that, the venture companies can raise lots of money, and then develop further.
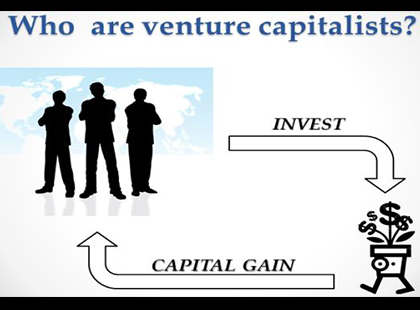
Why don’t venture companies borrow money from banks? Banks are reluctant to take risks in lending to venture companies because they are small, young, and unstable. So it is difficult for venture companies to raise funds from banks, and they try to raise funds from people called venture capitalists.
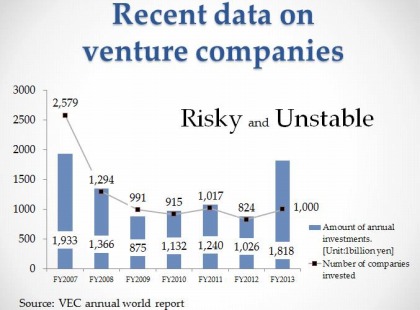
Do you know what has happened to venture companies after the financial global crisis caused by the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers? We found some data. From this graph, we can see that the changes in amount of annual venture capital investments and the numbers of companies invested by venture capitalists had both decreased dramatically till around 2012, because of the global financial crisis. But in 2013, the world market recovered quite a lot from the crisis. So we can say although the bad influence of the financial crisis has not finished yet, venture capital industry still has lots of possibilities.
Developing new technology and making new products are important and necessary for venture companies. If their businesses are becoming successful, the venture companies also want to go IPO. IPO means Initial Public Offering. By that, the venture companies can raise lots of money, and then develop further.
Why don’t venture companies borrow money from banks? Banks are reluctant to take risks in lending to venture companies because they are small, young, and unstable. So it is difficult for venture companies to raise funds from banks, and they try to raise funds from people called venture capitalists.
Do you know what has happened to venture companies after the financial global crisis caused by the bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers? We found some data. From this graph, we can see that the changes in amount of annual venture capital investments and the numbers of companies invested by venture capitalists had both decreased dramatically till around 2012, because of the global financial crisis. But in 2013, the world market recovered quite a lot from the crisis. So we can say although the bad influence of the financial crisis has not finished yet, venture capital industry still has lots of possibilities.
What are economic benefits of intangible assets? (Juniors: Kong Junze, Song Yongtao and Masashi Doi)
The title of our presentation is “What are economic benefits of intangible assets”. We hope you will like our presentation and get to know something new about intangible assets.
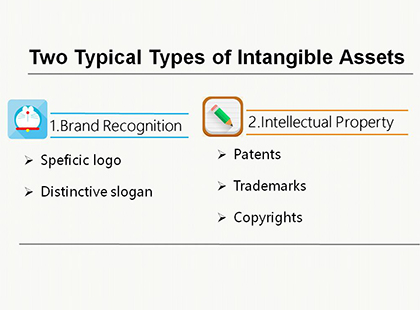
The first thing we would like to tell you about is the classification of intangible assets. There are two types of typical intangible assets. One is brand recognition. It includes specific logo and distinctive slogan. It makes people remember your company and buy your company's products. Another is intellectual property. It is composed of three parts, patents, trademarks and copyrights. For example, Adele has the copyrights to all of her songs. In other words, Adele can receive revenue whenever one of her songs is purchased.
It is noteworthy that none of brand recognition, copyrights, trademarks and patents has a physical aspect, but they are valuable because they can bring about a future financial benefit.
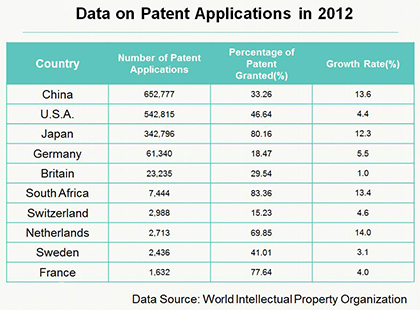
Next, let’s look at some data on patent in 2012. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization, China, as a populous country, the number of patent applications is the largest. But its grant rate is not the highest, 33.26% of patent applications received approval. The country having the highest grant rate is South Africa, 83.36%, whose number of patent applications is the sixth in the world, 7444. In terms of the number of patent applications, the United States and Japan are the second and third, respectively. The grant rate of the United States is also not so high, but Japan's grant rate is the second in the world. As for the growth rate of patent applications, the highest is Holland. Next is China and South Africa.
In conclusion, we would like to emphasize that usually intangible assets are held for usage instead of for selling because they can create future economic benefits.
The first thing we would like to tell you about is the classification of intangible assets. There are two types of typical intangible assets. One is brand recognition. It includes specific logo and distinctive slogan. It makes people remember your company and buy your company's products. Another is intellectual property. It is composed of three parts, patents, trademarks and copyrights. For example, Adele has the copyrights to all of her songs. In other words, Adele can receive revenue whenever one of her songs is purchased.
It is noteworthy that none of brand recognition, copyrights, trademarks and patents has a physical aspect, but they are valuable because they can bring about a future financial benefit.
Next, let’s look at some data on patent in 2012. According to the World Intellectual Property Organization, China, as a populous country, the number of patent applications is the largest. But its grant rate is not the highest, 33.26% of patent applications received approval. The country having the highest grant rate is South Africa, 83.36%, whose number of patent applications is the sixth in the world, 7444. In terms of the number of patent applications, the United States and Japan are the second and third, respectively. The grant rate of the United States is also not so high, but Japan's grant rate is the second in the world. As for the growth rate of patent applications, the highest is Holland. Next is China and South Africa.
In conclusion, we would like to emphasize that usually intangible assets are held for usage instead of for selling because they can create future economic benefits.
How customers choose banks? (Sophomores: Bunno Hirohito, Shun Hibino and Seiya Shirakata)
In this presentation, we talk about how customers choose banks. Our conclusion is that customers usually choose banks having lower fees, higher interest rate for savings account, more friendly service and more branches.
The first thing we would like to tell you about is “fees paid to banks”. Fees mean the money that we need to pay to banks when we get financial services from banks. When we choose banks, why low fees are good? Because low fees mean low costs.
For example, if you want to withdraw money from your bank account, you need to pay fees to your bank for this withdrawal. If you want to withdraw 1000 yen, and the withdrawal fee is 400 yen, what you can really get is 600 yen. But if the withdrawal fee is lower, let’s say 100 yen, you can get more money. So, customers usually choose banks whose fees are low.
There are many kinds of financial products. For example, bank savings, bonds, stocks and so on. Here, we will focus on bank savings and explain to you how deposits work. Imagine that customers put their money into the bank now. In the future, they can get interest on their bank savings. So, when the interest rate becomes higher, you can get more interest, and your return will increase. This means that bank savings become more attractive to customers.
Next, we would like to show you the result of a customer’s survey. This chart shows how customers feel about the services provided by the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, Japan’s largest bank, in 2014. From this chart, we can know the following results:
About 31.7% of customers are satisfied because all staff is kind, friendly, and reliable. About 34.0% of customers are somewhat satisfied because it is easy to make transactions through the internet and the explanation of it is easy to understand. About 5.9% of customers are dissatisfied because the waiting time is too long.
Finally, we would like to tell you some information about branches of banks. For example, the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ has about 2253 branches. The number of branches is the largest in Tokyo, about 797 branches. Next is Aichi Prefecture, about 517 branches. The third largest in the number of branches is Osaka Prefecture, about 336 branches. But on the other hand, among 47 prefectures, there is only one branch in 7 prefectures. Therefore, we can say that the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ focuses its branches in major cities. Having more branches nearby is good for customers, because they can use the bank more conveniently.
The first thing we would like to tell you about is “fees paid to banks”. Fees mean the money that we need to pay to banks when we get financial services from banks. When we choose banks, why low fees are good? Because low fees mean low costs.
For example, if you want to withdraw money from your bank account, you need to pay fees to your bank for this withdrawal. If you want to withdraw 1000 yen, and the withdrawal fee is 400 yen, what you can really get is 600 yen. But if the withdrawal fee is lower, let’s say 100 yen, you can get more money. So, customers usually choose banks whose fees are low.
There are many kinds of financial products. For example, bank savings, bonds, stocks and so on. Here, we will focus on bank savings and explain to you how deposits work. Imagine that customers put their money into the bank now. In the future, they can get interest on their bank savings. So, when the interest rate becomes higher, you can get more interest, and your return will increase. This means that bank savings become more attractive to customers.
Next, we would like to show you the result of a customer’s survey. This chart shows how customers feel about the services provided by the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ, Japan’s largest bank, in 2014. From this chart, we can know the following results:
About 31.7% of customers are satisfied because all staff is kind, friendly, and reliable. About 34.0% of customers are somewhat satisfied because it is easy to make transactions through the internet and the explanation of it is easy to understand. About 5.9% of customers are dissatisfied because the waiting time is too long.
Finally, we would like to tell you some information about branches of banks. For example, the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ has about 2253 branches. The number of branches is the largest in Tokyo, about 797 branches. Next is Aichi Prefecture, about 517 branches. The third largest in the number of branches is Osaka Prefecture, about 336 branches. But on the other hand, among 47 prefectures, there is only one branch in 7 prefectures. Therefore, we can say that the Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi UFJ focuses its branches in major cities. Having more branches nearby is good for customers, because they can use the bank more conveniently.